Cause Of Foot Pain In The Arch
Plantar fasciitis can be a real pain in the foot. Plantar fasciitis is the medical term for inflammation of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot. If you?ve ever had pain in the bottom of your foot with the first few steps out of bed in the morning, you?ve probably had some experience with this painful condition. In active populations, plantar fasciitis is often associated with overuse or a sudden change in activity, and temporarily easing off of activity can be part of the solution. In more sedentary populations, weight gain is usually a major contributor to plantar fasciitis and a weight-loss plan could be of benefit. Whether you?re active or sedentary, however, previous foot injuries, poor arch support, or tight muscles around the foot can all predispose you to plantar fasciitis.

Causes
Having low or no arches is normal for some people. In these cases, flat feet are usually inherited and the feet are fairly flexible. Occasionally, flat feet can be caused by an abnormality that develops in the womb, such as a problem with a joint or where two or more bones are fused together. This is known as tarsal coalition and results in the feet being flat and stiff. Flat feet that develop in later life can be caused by a condition that affects the joints, such as arthritis, or an injury to a muscle, tendon or joint in the foot.
Symptoms
Typically, the sufferer of plantar fasciitis experiences pain upon rising after sleep, particularly the first step out of bed. Such pain is tightly localized at the bony landmark on the anterior medial tubercle of the calcaneus. In some cases, pain may prevent the athlete from walking in a normal heel-toe gait, causing an irregular walk as means of compensation. Less common areas of pain include the forefoot, Achilles tendon, or subtalar joint. After a brief period of walking, the pain usually subsides, but returns again either with vigorous activity or prolonged standing or walking. On the field, an altered gait or abnormal stride pattern, along with pain during running or jumping activities are tell-tale signs of plantar fasciitis and should be given prompt attention. Further indications of the injury include poor dorsiflexion (lifting the forefoot off the ground) due to a shortened gastroc complex, (muscles of the calf). Crouching in a full squat position with the sole of the foot flat on the ground can be used as a test, as pain will preclude it for the athlete suffering from plantar fasciitis, causing an elevation of the heel due to tension in the gastroc complex.
Diagnosis
In more difficult cases of plantar fasciitis you should see your foot health professional for a thorough examination. They will find out why your arch or heel pain occurred in the first place and devise a treatment plan to relieve your pain and prevent it from reoccurring. They will evaluate your feet, walking pattern (gait), shoes, activities, exercise methods, and other relevant information and then devise your treatment plan.
Non Surgical Treatment
In addition to relieving the pain by providing better metatarsal support for your feet, many doctors advise stretching and strengthening the muscles that surround the damaged or weakened tendons. This advice can prove especially effective in preventing the possible side effects of fallen arches, including: inflammation and discomfort in the ligaments of the sole, Achilles tendonitis, shin splints, calluses, and bunions. Like plantar fasciitis, left untreated, fallen arches can cause a domino effect that impacts your legs, hips, and back.

Surgical Treatment
There are two types of bone procedure for flat feet, those where bone cuts and bone grafts are used to alter the alignment by avoiding any joint structures, or joint invasive procedures (called fusions or arthrodeses) that remove a joint to reshape the foot. With joint fusion procedures, there are those procedures that involve non-essential joints of the foot versus those that involve essential joints. All bone procedures have their place in flat foot surgery, and Dr. Blitz carefully evaluates each foot to preserve as much motion and function while obtaining proper and adequate alignment. In many cases a flat foot reconstruction involves both soft tissue procedures and bone procedures to rebuild and restore the arch. There are several joints in the arch of the foot that can collapse - and these joints are non-essential joints of the foot. This does not mean that they do not have a purpose, but rather become inefficient is providing a stable platform for function. As such, locking these non-essential non-functioning joints into place is commonly recommended. These joints are fused together with screws and/or plates. A heel bone that is no longer in proper position and pushed outwards away from the foot can be corrected with a bone cut and realignment procedure, so long as the displacement is not too significant. A benefit of this surgery is that it keeps the back portion of the foot mobile, and helps the surrounding tendons work for efficiently in maintaining the arch. In certain flat feet, the foot is deviated outwards and away from the midline of the body. Sometimes, this is due to the outer portion of the foot being shorter than the inner portion. Here bone graft can be added to the outer edge of the foot to lengthen the foot to swing the foot over into a corrected position. This procedure is most commonly performed in children and young adults. A bone graft is inserted into the top part of the arch to realign a component of the flat foot, medically known as forefoot varus or medial column elevatus. The back part of the foot (called the rearfoot complex) can be the cause (or source) of the flat foot or the simply affected by the flat foot foot. In simple terms, the back part of the foot can be made to flatten out due to arch problems - and vica versa for that matter. Dr. Blitz specifically identifies the cause of the flat foot as this will determine the best treatment plan, as each flat foot needs to be evaluated individually. The rearfoot is made up of three joints, and depending on the extent and most importantly the rigidity of these joints, they may require fusion to restore alignment. When all three joints require fusion - this call is a triple arthrodesis. For completeness, isolated fusion of any of the three joints can be performed (such as subtalar joint arthrodesis, talonavicular arthrodesis, and calcaneaocuboid joint arthrodesis). The medical decision making for isolated fusions is beyond the scope this article, but Dr. Blitz tries to avoid any rearfoot fusion for flexible feet because these are joints are essential joints of the foot, especially in younger people. Those in severe cases, it may be advantageous to provide re-alignment.
Prevention
Maintain a healthy weight, Use insoles to support your arches, Limit how often you wear high heels, Use proper shoes, especially when exercising to evenly distribute weight through your foot.
Stretching Exercises
Strength training and stretching can help avoid injury and keep your feet free from pain. Stretching should focus on the bottom of your foot to loosen tissues and tight ligaments surrounding your arch. The easiest way to do this is by grabbing a towel and sitting on the floor. You can do this while you catch up on the news in the morning, or when you get home from work. Put one leg out in front with your foot flexed up. Loop the towel around the ball of your foot and gently pull your toes towards you. Hold for thirty seconds and then repeat 3-4 times before switching feet.
Achilles Tendon Tear Treatments
Overview  A torn or ruptured Achilles tendon is simply no fun at all. This essential cord of strong, fibrous material attaches the heel bone to the calf muscles and is used in just about every movement, from walking and running to jumping and standing on your tip-toes. It also helps bend the foot downwards at the ankle. As the strongest tendon in the body, the Achilles can withstand a force of about 1,000 pounds. About 7 out of every 100,000 people will suffer from a ruptured Achilles at some point in time, with over 80% of these injuries occurring during a recreational sports activity. Athletes have a 24% chance of tearing their Achilles, but competitive runners have a 40 to 50% chance of Achilles tendon rupture during their lifetime. Causes Repeated stress from a variety of causes is often the cause of Achilles tendon injury. The stress may occur from any of the following. Excessive activity or overuse. Flat feet. Poorly fitting or inadequate shoes. Inadequate warm-up or proper conditioning. Jogging or running on hard surfaces. Older recreational athlete. Previous Achilles tendon injury (tendonitis/rupture). Repeated steroid injections. Sudden changes in intensity of exercise. Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (especially in children). Trauma to the ankle. Tense calf muscles prior to exercise. Weak calf muscles. Symptoms A sudden and severe pain may be felt at the back of the ankle or calf, often described as "being hit by a rock or shot" or "like someone stepped onto the back of my ankle." The sound of a loud pop or snap may be reported. A gap or depression may be felt and seen in the tendon about 2 inches above the heel bone. Initial pain, swelling, and stiffness may be followed by bruising and weakness. The pain may decrease quickly, and smaller tendons may retain the ability to point the toes. Without the Achilles tendon, though, this would be very difficult. Standing on tiptoe and pushing off when walking will be impossible. A complete tear is more common than a partial tear. Diagnosis A doctor will look at the type of physical activity you have been doing. He or she will then look at your foot, ankle and leg. An MRI may also be used. This is to help determine the severity of the tear and the extent of separation of the fibers. Non Surgical Treatment Not every torn Achilles tendon needs an operation. Recent studies have shown that even a conservative treatment, i.e. immobilizingt the leg can lead to satisfactory healing successes. This requires, however, that the patient is fitted with a cast (immobilization splint) and/or a special boot for a period of approximately 6 - 8 weeks. After that, the boot must be worn during the day for about two more weeks. An intensive physiotherapy will start after about six weeks to train the calf muscles so that the initial coordination can be restored. Running training on flat ground can be started again after another 10 - 12 weeks. Studies show that the danger of a recurring torn tendon is higher after a conservative treatment opposed to an operative treatment. Depending on the type of treatment, about 10 - 15 percent of those affected can expect at some point to again suffer from a tear of the Achilles tendon. Moreover, in the non-operated cases, we see more often a significant permanent weakness of the footprint, particularly restricting the ability to participate in sports.
A torn or ruptured Achilles tendon is simply no fun at all. This essential cord of strong, fibrous material attaches the heel bone to the calf muscles and is used in just about every movement, from walking and running to jumping and standing on your tip-toes. It also helps bend the foot downwards at the ankle. As the strongest tendon in the body, the Achilles can withstand a force of about 1,000 pounds. About 7 out of every 100,000 people will suffer from a ruptured Achilles at some point in time, with over 80% of these injuries occurring during a recreational sports activity. Athletes have a 24% chance of tearing their Achilles, but competitive runners have a 40 to 50% chance of Achilles tendon rupture during their lifetime. Causes Repeated stress from a variety of causes is often the cause of Achilles tendon injury. The stress may occur from any of the following. Excessive activity or overuse. Flat feet. Poorly fitting or inadequate shoes. Inadequate warm-up or proper conditioning. Jogging or running on hard surfaces. Older recreational athlete. Previous Achilles tendon injury (tendonitis/rupture). Repeated steroid injections. Sudden changes in intensity of exercise. Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (especially in children). Trauma to the ankle. Tense calf muscles prior to exercise. Weak calf muscles. Symptoms A sudden and severe pain may be felt at the back of the ankle or calf, often described as "being hit by a rock or shot" or "like someone stepped onto the back of my ankle." The sound of a loud pop or snap may be reported. A gap or depression may be felt and seen in the tendon about 2 inches above the heel bone. Initial pain, swelling, and stiffness may be followed by bruising and weakness. The pain may decrease quickly, and smaller tendons may retain the ability to point the toes. Without the Achilles tendon, though, this would be very difficult. Standing on tiptoe and pushing off when walking will be impossible. A complete tear is more common than a partial tear. Diagnosis A doctor will look at the type of physical activity you have been doing. He or she will then look at your foot, ankle and leg. An MRI may also be used. This is to help determine the severity of the tear and the extent of separation of the fibers. Non Surgical Treatment Not every torn Achilles tendon needs an operation. Recent studies have shown that even a conservative treatment, i.e. immobilizingt the leg can lead to satisfactory healing successes. This requires, however, that the patient is fitted with a cast (immobilization splint) and/or a special boot for a period of approximately 6 - 8 weeks. After that, the boot must be worn during the day for about two more weeks. An intensive physiotherapy will start after about six weeks to train the calf muscles so that the initial coordination can be restored. Running training on flat ground can be started again after another 10 - 12 weeks. Studies show that the danger of a recurring torn tendon is higher after a conservative treatment opposed to an operative treatment. Depending on the type of treatment, about 10 - 15 percent of those affected can expect at some point to again suffer from a tear of the Achilles tendon. Moreover, in the non-operated cases, we see more often a significant permanent weakness of the footprint, particularly restricting the ability to participate in sports.  Surgical Treatment Referral to a surgeon for open or percutaneous repair of the tendon is often necessary, followed by an immobilisation period. Functional bracing and early mobilisation are becoming more widely used postoperatively. There is no definitive protocol for this and it may differ, depending on the surgeon. Operative treatment has a reduced chance of re-rupture compared with conservative treatment (3.5% versus 12.6%) and a higher percentage of patients returning to the same level of sporting activity (57% versus 29%). The patient's desired functional outcome and comorbidities that affect healing will be factors in the decision to operate.
Surgical Treatment Referral to a surgeon for open or percutaneous repair of the tendon is often necessary, followed by an immobilisation period. Functional bracing and early mobilisation are becoming more widely used postoperatively. There is no definitive protocol for this and it may differ, depending on the surgeon. Operative treatment has a reduced chance of re-rupture compared with conservative treatment (3.5% versus 12.6%) and a higher percentage of patients returning to the same level of sporting activity (57% versus 29%). The patient's desired functional outcome and comorbidities that affect healing will be factors in the decision to operate.
Pes Planus?

There are many different causes of and treatments for flat foot. The most important part of treatment is determining the exact flat foot type on an individual basis, and doing so early on. The main objective is to become educated on the potential problems, so that you can stop them before they start. Conservative treatment is often successful if initiated early. The old adage "a stitch in time saves nine" definitely applies to the human body, hopefully more figuratively than literally. Do not ignore what your common sense and your body are telling you. Yes, you can live without an arch, but never neglect a symptomatic foot. If you neglect your feet, they will make you pay with every literal step you take.
Causes
The most common acquired flat foot in adults is due to Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. This develops with repetitive stress on the main supporting tendon of the arch over a long period of time. As the body ages, ligaments and muscles can weaken, leaving the job of supporting the arch all to this tendon. The tendon cannot hold all the weight for long, and it gradually gives out, leading to a progressively lower arch. This form of flat foot is often accompanied by pain radiating behind the ankle, consistent with the course of the posterior tibial tendon. Compounding matters is the fact that the human foot was not originally designed to withstand the types of terrain and forces it is subjected to today. Nowhere in nature do you see the flat hard surfaces that we so commonly walk on in present times. Walking on this type of surface continuously puts unnatural stress on the arch. The fact that the average American is overweight does not help the arch much either-obesity is a leading cause of flat feet as the arch collapses under the excessive bodyweight. Furthermore, the average life span has increased dramatically in the last century, meaning that not only does the arch deal with heavy weight on hard flat ground, but also must now do so for longer periods of time. These are all reasons to take extra care of our feet now in order to prevent problems later.
Symptoms
A significant number of people with fallen arches (flat feet) experience no pain and have no problems. Some, however, may experience pain in their feet, especially when the connecting ligaments and muscles are strained. The leg joints may also be affected, resulting in pain. If the ankles turn inwards because of flat feet the most likely affected areas will be the feet, ankles and knees. Some people have flat feet because of a developmental fault during childhood, while others may find that the problem develops as they age, or after a pregnancy. There are some simple devices which may prevent the complications of flat feet.
Diagnosis
You can always give yourself the ?wet test? described above to see whether you have flat feet. Most people who do not notice their flat feet or have no pain associated with them do not think to see a foot doctor. Flat feet can lead to additional problems such as stiffness or pain, however, especially if the condition appears out of nowhere. If you think you may have flat feet, you should seek medical attention to ensure there are no additional issues to worry about. Your doctor will be able to diagnose you with a number of tests. For example, he or she may have you walk around, stand still, or stand on your tiptoes while you are being examined. Your doctor may also examine your foot?s shape and functionality. It?s important to let your foot doctor know about your medical and family history. In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests such as x-rays or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to determine a cause of your flat foot. If tarsal coalition is suspected in children, a CT scan is often ordered.
Non Surgical Treatment
Switch activities for a little while. If you?re a super athlete, you don?t want to hear that you need to take a break, but there?s no way around it. You need to lay off the high impact sports like basketball, tennis and running. Don?t panic-there?s no shortage of alternatives. Find a high school track that?s open to the public and try going for a run. Many athletic programs use spongy synthetic materials to pave tracks instead of concrete. This is much easier on all the joints and tendons, not only in your feet but your legs and ankles. You can also try running on dirt trails or stable grassy areas. Take up swimming for a little while. This is actually an ideal activity for your arches. The buoyancy of water takes weight off our feet, but still allows for aerobic activity. Many gyms and activity centers also offer various water sport classes. In no time flat, you?ll be on your way to healthier feet.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
Prevention
Strap the arches into the anatomically correct positions with athletic tape and leave them like this for some time. If the fallen arches are an issue with the muscular structure, this may give the muscles an opportunity to strengthen. This is definitely not a fallen arches cure all the time but it can help prevent it more times than not. Ask a doctor or physical therapists to show you how to do this taping. Find shoes that fit. This may require that you get your foot measured and molded to ensure that the shoe will fit. Shoes that are too big, too tight or too short, may not directly cause the fallen arches, but they can assist with the damage to the area. These shoes should have thick cushioning inside and have plenty of room for your toes. Walk without shoes as much as possible. Shoes directly assist with weakening and distorting the arches of the feet so going without shoes can actually help strengthen your arches and prevent fallen arches. Walking on hard and bumpy surfaces barefooted makes the muscles in your feet strengthen in order to prevent injury. It is a coping mechanism by your body. Insert heel cups or insoles into the shoes that you wear the most. Many people wear uncomfortable shoes to work and these are the same shoes that cause their arches the most problems. Inserting the heel cups and insoles into these shoes can prevent fallen arches from occurring. Many people place these inserts into all their shoes to ensure support. Ask a medical professional, either your doctor or a physical therapist, about daily foot exercises that may keep the arches stronger than normal. Many times, you can find exercises and stretches on the Internet on various websites. Curling your toes tightly and rotating your feet will help strengthen your longitudinal arches. Relax your feet and shake them for a minute or so before you do any arch exercises. This will loosen the muscles in your feet that stay tight due to normal daily activities. Wear rigid soled sandals whenever possible to provide a strong support for your arches. Wooden soled sandals are the best ones if available. Walk or jog on concrete as much as you can. This will create a sturdy support for your arches. Running or walking in sandy areas or even on a treadmill, does not give rigid support. Instead, these surfaces absorb the step, offering no support for arches.
Pain In The Arch Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often persistent kind of repetitive strain injury afflicting runners, walkers and hikers, and nearly anyone who stands for a living, cashiers, for instance. It causes mainly foot arch pain and/or heel pain. Morning foot pain is a signature symptom. Plantar fasciitis is not the same thing as heel spurs and flat feet, but they are related and often confused. Most people recover from plantar fasciitis with a little rest, arch support (regular shoe inserts or just comfy shoes), and stretching, but not everyone. Severe cases can stop you in your tracks, undermine your fitness and general health, and drag on for years.

Causes
Having low or no arches is normal for some people. In these cases, flat feet are usually inherited and the feet are fairly flexible. Occasionally, flat feet can be caused by an abnormality that develops in the womb, such as a problem with a joint or where two or more bones are fused together. This is known as tarsal coalition and results in the feet being flat and stiff. Flat feet that develop in later life can be caused by a condition that affects the joints, such as arthritis, or an injury to a muscle, tendon or joint in the foot.
Symptoms
The groups of muscles that support the arch can be divided into two groups. The muscles on the top of the arch start on the front lower leg and help to lift the arch, and the muscles that help pull the arch on the bottom of the foot are located the on back of the lower leg. Muscle injury may be indicated when pain is felt when the foot is fully extended, flexed, or turned in or out. Pain may also be felt when working the foot against resistance. Bruises are the result of a direct-force injury to the body. A bruise can occur to the foot by a variety of causes, such as having your foot stepped on or by stepping on a rock. The tissues that compose the arch do not provide that area of the body much protection. Blows to the foot that result in pain, discoloration, swelling, and changes in how you walk may indicate more serious damage.
Diagnosis
In people with flat feet, the instep of the foot comes in contact with the ground when standing. To diagnose the problem, the health care provider will ask you to stand on your toes. If an arch forms,the flat foot is called flexible. You will not need any more tests or treatment. If the arch does not form with toe-standing (called rigid flat feet), or if there is pain, other tests may be needed, including a CT scan to look at the bones in the foot. MRI scan to look at the tendons in the foot. X-ray of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most effective treatment for foot arch pain and strain is to use an arch support. The arch support sits under the foot and stops the arch of the foot from collapsing, thereby preventing the stretch of the arch pad which causes pain and discomfort. Wearing an arch support in slippers or house shoes can also prevent pain in the mornings when discomfort it most common and severe. Arch supports usually relieve symptoms within a few days.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered only after 12 months of aggressive nonsurgical treatment. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the plantar fascia, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite a year of calf stretches. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope, an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Plantar fascia release. If you have a normal range of ankle motion and continued heel pain, your doctor may recommend a partial release procedure. During surgery, the plantar fascia ligament is partially cut to relieve tension in the tissue. If you have a large bone spur, it will be removed, as well. Although the surgery can be performed endoscopically, it is more difficult than with an open incision. In addition, endoscopy has a higher risk of nerve damage. The most common complications of release surgery include incomplete relief of pain and nerve damage. Most patients have good results from surgery. However, because surgery can result in chronic pain and dissatisfaction, it is recommended only after all nonsurgical measures have been exhausted.
Prevention
Because most cases of flatfeet are inherited, the condition is usually impossible to prevent. Even when children with flexible flatfeet are treated with arch supports and corrective shoes, there is little evidence that these devices prevent the condition from lasting into adulthood.
What Can Easily cause Adult Aquired Flat Foot ?
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is definitely an inflammation and also / or overstretching in the posterior tibial tendon in the foot. An important function of the posterior tibial tendon is to aid offer the arch. Yet throughout PTTD, your tendon?s ability to perform that occupation is actually impaired, frequently resulting in the flattening in the foot. PTTD can be usually known as ?adult-acquired flatfoot? since it will always be the most common kind involving flatfoot developed during adulthood. Though this issue typically happens in only 1 foot, some people may develop it inside each feet. PTTD is actually typically progressive, which means it will keep obtaining worse-especially if it isn?t handled early. This differs via versatile flatfoot because flexible flatfoot typically begins when they might be young or even adolescence along with continues in to adulthood. That typically happens in each feet and usually progresses in severity throughout the particular adult years. Because your deformity worsens, the actual soft tissues (tendons and also ligaments) with the arch might stretch or perhaps tear and flip into inflamed. The Particular term ?flexible? implies that as the foot is actually flat when standing (weight bearing), the actual arch returns when not necessarily standing. Throughout your first stages of versatile flatfoot arthritis is not restricting motion of the arch and also foot, nevertheless inside the later phases arthritis could develop to this type of point the arch and also foot grow to be stiff.
Causes
The most typical cause regarding acquired adult flatfoot will be posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Exactly what causes adult acquired flat foot? Fracture or even dislocation. Tendon laceration. Tarsal Coalition. Arthritis. Neuroarthropathy. Neurological weakness.
Symptoms
At initially you might discover pain as well as swelling across the medial (big toe) aspect with the foot. This is the area exactly where the posterior tibialis tendon travels from your back again with the leg beneath your medial ankle bone to the foot. As your situation will get worse, tendon failure occurs as well as the pain gets worse. some patients experience pain along the lateral (outside) side of your foot, too. An Individual might find that you hurt at the end of your day or perhaps following long intervals regarding standing. A Few individuals with this particular situation have got difficulty rising up on their own toes. They Will may become struggling to participate completely in sports or other recreational activities.
Diagnosis
Your podiatrist is extremely acquainted with tendons that have just concerning had enough, and will likely always be capable of diagnose this situation simply by conducting a physical exam of one's foot. He or perhaps she will most likely look at the location visually and by feel, will inquire regarding your own medical history (including past pain or injuries), along with may also observe the feet when you walk. you might also be inspired to attempt standing on your own own toes. This might be completed by having an individual lift the ?good? foot (the one without the particular complaining tendon) off the ground, standing just on your difficulty foot. (You may end up being instructed to place both hands contrary to the wall to aid using balance.) Then, your current podiatrist will ask an individual to make an effort to increase on your toes about the negative foot. If you have problems doing so, it might indicate an issue together along with your posterior tibial tendon. A Quantity Of imaging technologies could be used to diagnose this condition, although it?s more likely the physician will rely primarily on an actual exam. However, he or she might order scans such being an MRI or even CT scan to look in the foot?s interior, and also X-rays may well even be helpful in a diagnosis.
Non surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment also depends around the stage of the disease. Early on, the anguish as well as swelling without deformity may always be treatable using rest, ice, compression, elevation along with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Generally OTC orthotic inserts are generally advised along with stability oriented athletic shoes. If this fails or possibly the issue is a entire lot more advanced, immobilization in the rigid strolling boot is recommended. This rests your tendon and also protects it from further irritation, attenuation, or perhaps tearing. If signs are greatly improved as well as eliminated then your affected person could go again to a supportive shoe. To End Up Being Able To protect your individual coming from reoccurrence, different kinds of tools are recommended. the most typical device can be orthotics. Typically custom-made orthotics are usually far better OTC. That They tend to be reserved pertaining to early staged PTTD. Advanced phases may require a more aggressive type orthotic or an AFO (ankle-foot orthosis). Right now there are different kinds of AFO's. 1 kind includes a double-upright/stirrup attached to a footplate. An Additional is truly a gauntlet-type with a custom plastic interior surrounded be considered a lace-up leather exterior. Each need the use of the cumbersome kind athletic or even orthopedic shoes. Individual compliance is usually challenging using these larger braces as well as shoes.

Surgical Treatment
When conservative treatment fails surgical intervention is offered. Pertaining To a new Stage one deformity a new posterior tibial tendon tenosynovectomy (debridement with the tendon) or primary repair might become indicated. Regarding Stage two the combination of Achilles lengthening using bone cuts, calcaneal osteotomies, and tendon transfers can be common. Stage two flexible PTTD is the most common stage patients present together with pertaining to treatment. in Stage three or 4 PTTD isolated fusions, locking a pair of or perhaps much more joints together, maybe indicated. Most remedy is dependent around the stage as well as severity at presentation with most the objectives and also exercise quantity regarding a individual inside mind. treatment will be customized to the individual patient needs.
Pain In The Arch Causes Symptoms And Treatments
The arch functions as a shock absorber for our entire body. Each time we step down, we place up to 5 times our body weight on the foot, depending on whether we are walking, running, or jumping. If there were no shock absorber in the foot, the force of each step would fracture or dislocate the bones of the foot, leg, and lower back. When pain occurs in the arch, it is telling us it is "sick" and cannot function properly. If left untreated, it can cause constant pain throughout the entire foot, and eventually the knee, hip, and lower back.

Causes
The most common cause of arch pain is plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis is the name that describes inflammation of the fibrous band of tissue that connects the heel to the toes. Symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain early in the morning and pain with long walks or prolonged standing. Arch pain early in the morning is due to the plantar fascia becoming contracted and tight as you sleep through the night. When awakening and walking in the morning, the fascia is still tight and prone to irritation when stretched. When walking or standing for long periods, the plantar fascia becomes inflamed and painful. Treatment of plantar fasciitis is best accomplished with some simple stretching exercises, anti-inflammatory medications, and inserts for your shoes.
Symptoms
Pain in arch of foot is really the only symptom of this condition. It is unlikely to see any swelling or bruising and instead there will be a deep tender spot near the heel. Occasionally the pain may radiate further down the foot. With this condition, pain will usually be felt first thing in the morning or after periods of sitting. This is because the plantar fascia tightens and shortens slightly when there is no weight on it and by standing on it it suddenly stretches and becomes painful. After a few steps it starts to loosen off and the pain may subside. If this is the same pattern of pain you experience it is quite likely you have plantar fasciits. Pain may also be felt when walking up stairs or standing on tip-toes (anything that stretches the fascia).
Diagnosis
In more difficult cases of plantar fasciitis you should see your foot health professional for a thorough examination. They will find out why your arch or heel pain occurred in the first place and devise a treatment plan to relieve your pain and prevent it from reoccurring. They will evaluate your feet, walking pattern (gait), shoes, activities, exercise methods, and other relevant information and then devise your treatment plan.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most effective treatment for foot arch pain and strain is to use an arch support. The arch support sits under the foot and stops the arch of the foot from collapsing, thereby preventing the stretch of the arch pad which causes pain and discomfort. Wearing an arch support in slippers or house shoes can also prevent pain in the mornings when discomfort it most common and severe. Arch supports usually relieve symptoms within a few days.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical advances have dramatically improved the ability to alleviate the pain and decreased function that millions of Americans experience due to flat feet. Nevertheless, many patients and even some physicians remain unaware of the new procedures, which are best performed by a foot and ankle specialist who has the applicable training and experience.
Prevention
Strap the arches into the anatomically correct positions with athletic tape and leave them like this for some time. If the fallen arches are an issue with the muscular structure, this may give the muscles an opportunity to strengthen. This is definitely not a fallen arches cure all the time but it can help prevent it more times than not. Ask a doctor or physical therapists to show you how to do this taping. Find shoes that fit. This may require that you get your foot measured and molded to ensure that the shoe will fit. Shoes that are too big, too tight or too short, may not directly cause the fallen arches, but they can assist with the damage to the area. These shoes should have thick cushioning inside and have plenty of room for your toes. Walk without shoes as much as possible. Shoes directly assist with weakening and distorting the arches of the feet so going without shoes can actually help strengthen your arches and prevent fallen arches. Walking on hard and bumpy surfaces barefooted makes the muscles in your feet strengthen in order to prevent injury. It is a coping mechanism by your body. Insert heel cups or insoles into the shoes that you wear the most. Many people wear uncomfortable shoes to work and these are the same shoes that cause their arches the most problems. Inserting the heel cups and insoles into these shoes can prevent fallen arches from occurring. Many people place these inserts into all their shoes to ensure support. Ask a medical professional, either your doctor or a physical therapist, about daily foot exercises that may keep the arches stronger than normal. Many times, you can find exercises and stretches on the Internet on various websites. Curling your toes tightly and rotating your feet will help strengthen your longitudinal arches. Relax your feet and shake them for a minute or so before you do any arch exercises. This will loosen the muscles in your feet that stay tight due to normal daily activities. Wear rigid soled sandals whenever possible to provide a strong support for your arches. Wooden soled sandals are the best ones if available. Walk or jog on concrete as much as you can. This will create a sturdy support for your arches. Running or walking in sandy areas or even on a treadmill, does not give rigid support. Instead, these surfaces absorb the step, offering no support for arches.
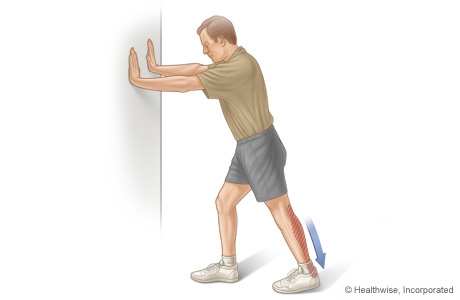
Stretching Exercises
Calf Raises. Strengthens the tendons in your heels and calf muscles, which support your arch. Raise up on the balls of your feet as high as possible. Slowly lower down. Do three sets of 10 reps. Progress to doing the raises on stairs (with heels hanging off), and then to single-leg raises. Step Stretch. Improves flexibility in your Achilles tendon and calf-when these areas become tight, the arch gets painfully overloaded. Stand at the edge of a step, toes on step, heels hanging off. Lower your heels down, past the step, then raise back up to the start position. Do three sets of 10 reps. Doming. Works the arch muscles and the tibialis posterior (in the calf and foot) to control excess pronation. While standing, press your toes downward into the ground while keeping the heel planted, so that your foot forms an arch (or dome). Release, and do three sets of 10 reps on each foot. Toe Spread and Squeeze. Targets the interossei muscles of the foot, which support the arch. While sitting, loop a small resistance band around your toes. Spread toes; release. Then place a toe separator (used at nail salons) in between toes. Squeeze toes in; release. Do three sets of 10 reps of each exercise on both feet. Towel Curls. Works the toe-flexor muscles that run along your arch to increase overall foot strength. Lay a small hand towel on the floor, and place one foot on the towel. Using just your toes, scrunch the towel toward you, hold, then slowly push the towel away from you back to start position. Do three sets of 10 reps on each foot.
Managing With Arch Pain
We all experience sore arches now and again after a long hike, standing in a long line or walking from one end to the other of a big shopping mall. It's normal for feet to get tired out sometimes, and there's usually no need to worry unless the pain persists. If you're turning to the web because it's dawning on you that your arches are sore several days a week, or maybe even every day, you're doing a smart thing. Chronic pain in the arches can actually be a symptom of a significant underlying condition called Plantar Fasciitis that requires attention and treatment to prevent it from worsening. This article will quickly point out what you need to know about arch pain and Plantar Fasciitis and provide you with resources for learning how to recover.
Causes
The causes of high arched feet can vary greatly. They range from neurological disorders, club foot, injury, and often times there may be no known reason. The idea behind surgery to correct this often painful condition is to bring the arch down and thereby, allow the ground pressure of walking to be more evenly distributed across the entire bottom of the foot. Over time high arch feet can cause severe plantar calluses, ulcerations broken metatarsals and even chronically sprained ankles.
Symptoms
Pain in arch of foot is really the only symptom of this condition. It is unlikely to see any swelling or bruising and instead there will be a deep tender spot near the heel. Occasionally the pain may radiate further down the foot. With this condition, pain will usually be felt first thing in the morning or after periods of sitting. This is because the plantar fascia tightens and shortens slightly when there is no weight on it and by standing on it it suddenly stretches and becomes painful. After a few steps it starts to loosen off and the pain may subside. If this is the same pattern of pain you experience it is quite likely you have plantar fasciits. Pain may also be felt when walking up stairs or standing on tip-toes (anything that stretches the fascia).
Diagnosis
Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment isn't usually needed for flat feet because the condition doesn't usually cause any significant problems. Aching feet can often be relieved by wearing supportive shoes that fit properly. You may need to wear shoes that are wider than normal. If your feet overpronate, you may need to wear a special insole (an orthotic) inside your shoes to stop your feet rolling inwards when you walk or run. These will usually need to be made and fitted by a podiatrist.

Surgical Treatment
Tendon transfers: Too much pull of certain muscles and tendons is often the cause of the deformity related with a cavus foot. Moving one of these muscles or tendons may help the foot work better. In addition, patients with a cavus foot may have weakness in moving the foot up, which is sometimes called a foot drop. In these cases, a tendon from the back of the ankle may be moved to the top of the foot to help improve strength. Correcting the deformity of the foot may not be possible with soft tissue procedures alone. In these instances, one or more bone cuts (osteotomies) may be needed. Instead of a bone cut, a fusion (arthrodesis) procedure may be used. A fusion removes the joint between two bones so they grow together over time. During a fusion the bones may be held in place with plates or screws. Calcaneal osteotomy: This procedure is performed to bring the heel bone back under the leg. This is needed if correction of the deformity in the front of the foot does not also correct the back of the foot or ankle. A calcaneal osteotomy can be performed several ways and is often held in place with one or more screws. Sometimes patients have a deformity that has caused damage to the joints. In these cases, soft tissue procedures or bone cuts may not be enough, and it may be necessary to eliminate the joint. Clawed toes are a common problem with cavus foot deformity. This can be treated with tendon surgery, fusion or removal of part of the toe bones. Following surgery the toes are often temporarily held in place with pins.
Stretching Exercises
Gastroc stretch. Stand on the edge of a step. Rise slowly on your toes. Lower yourself slowly as far as you can until you feel a stretch in your calf. Don?t roll your foot inward or outward. Hold for 1-2 seconds. Reps:10-20 (stop before you fatigue). Soleus stretch. Same as above, but start with your knee bent so that you feel a slight stretch in your calf or achilles. Maintain the angle of your knee throughout the stretch. Bicycle stretch. Lie on your side. Keeping your top leg straight, bring your knee toward your nose until you feel a slight stretch in the hamstring. Maintaining this angle at your hip, start pretending you are pedalling a bicycle with the top leg. Make sure you feel a slight stretch each time your knee is straight. Reps: 10-30 for each leg. If you feel any pops or clicks in your hip or back, try raising the top leg a little (making the thighs further apart) to eliminate the popping. Foot Intrinsic Exercises. Assisted metatarsal head raising. Sit in a chair. Find the bumps at the ball of your foot just before your big toe and just before the little toe. These are the first (big toe) and fifth (little toe) metatarsal heads. Place your second and third fingers from one hand under the first metatarsal head, and the second and third fingers from the other hand under the fifth metatarsal head. Now lay the thumbs from each hand in a diagonal across your toes so that they form a right angle meeting at the nail of the second toe. Your hands are now in position to assist your toes. Keep your toes straight, with the toe pads on the floor. Use your fingers to help raise all the metatarsal heads (the ball of your foot). Do not let your toes curl under keep them long. Now relax. Reps 7-10 for each foot. As this exercise gets easier, let your fingers do less of the work until your toes can do the exercise unassisted. This can take up to three weeks. When your strength has improved to this point, you can progress to the following three exercises, which are best done in stocking feet on a slippery floor. Active metatarsal head raising. Stand with your weight on both feet. Raise your metatarsal heads (the ball of your foot) while keeping your toes from curling under and maintaining your heel on the ground. Relax. Reps 6-7. Do one foot at a time. If you do more reps than you are ready for, you may well develop cramping in your foot. I once had a client who thought if seven reps were good, 10 were better. For good measure, she did the 10 reps 10 times in a day, and then she was unable to walk the next day from having used a set of muscles she had never exercised before. Don?t overdo it.